Exploring the Intriguing World of Quantum Biology
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Quantum Biology
Quantum biology investigates the potential influence of quantum mechanics on biological processes. Unlike the conventional aspects of quantum theory that underpin standard chemistry and biology—like orbitals and valence shells—quantum biology delves into phenomena such as tunneling, superposition, and entanglement. While these ideas are captivating, many models are still in the speculative stage and require further evidence to confirm whether these unconventional quantum effects truly drive biological phenomena.
A fundamental question arises: how can these quantum effects manifest within biological time frames and in warm, wet, and chaotic environments? Presently, the only established method for facilitating such effects involves cooling systems to near absolute zero temperatures.
Section 1.1: The Concept of Quantum Tunneling
Quantum tunneling refers to the ability of particles, particularly at atomic scales like electrons, to pass through energy barriers. It's akin to a ball that, in addition to bouncing off a window, can occasionally appear on the other side without breaking the glass.
Where is this observed? Enzymes have been confirmed to accelerate reactions through quantum tunneling, establishing a clear connection. Additionally, there is speculation that quantum tunneling might contribute to genetic mutations and play a role in our sense of smell, alongside the traditional lock-and-key model.
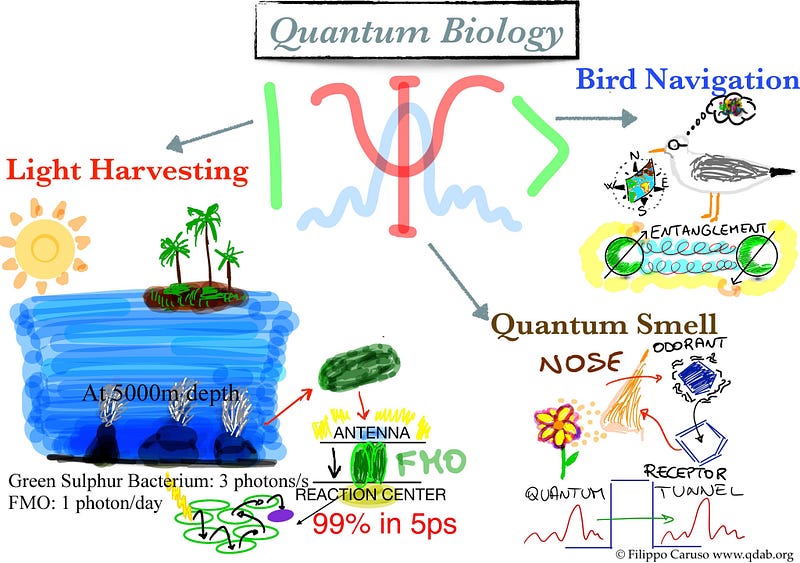
Chapter 2: The Phenomenon of Quantum Coherence
In the realm of photosynthesis, it's posited that the conversion of light into chemical energy may involve the simultaneous traversal of various pathways from light capture to the reaction center where energy is transformed.
Section 2.1: The Intricacies of Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement describes a situation where two particles, even when separated, remain interconnected; changes to one instantly affect the other, without any causal communication channel.
This phenomenon has been observed in the navigation abilities of the European robin, which appears to utilize entangled radicals in a molecule, triggered by light, to sense the Earth's magnetic field.
Section 2.2: Historical Perspectives on Quantum Biology
The exploration of quantum effects in biological systems, despite their typically warm, moist, and disordered nature, was first suggested by Erwin Schrödinger, a pioneer in quantum theory. Notably, theories proposing a quantum basis for consciousness, including those by Roger Penrose, have sparked further interest in this interdisciplinary field.
As we continue to investigate, the question remains: do these counterintuitive aspects of quantum mechanics influence biological processes broadly, or are they isolated phenomena deserving of the title "quantum biology"?
The second video, titled "What the hell is Quantum Biology?" offers an engaging exploration of these concepts.
References
- Erwin Schrödinger, Roger Penrose: What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical Sketches (Canto Classics).
- Articles on quantum coherence and quantum tunneling in biological systems.
- YouTube: An Introduction to Quantum Biology - with Philip Ball.
- YouTube: What the hell is Quantum Biology?