Harnessing Chainlink: Connecting Blockchain to Real-World Data
Written on
Understanding Chainlink's Role
Hello, crypto enthusiasts! It's been a while since my last update, and I appreciate your patience as I've been quite occupied. In this piece, we'll delve into Chainlink—a groundbreaking project that serves as a bridge between real-world information and blockchain technology, which is crucial for broader adoption. We'll examine key facets of this initiative, so let's get started!
What Exactly is Chainlink?
Chainlink is a framework that enables smart contracts to access external data. This is achieved through an "Oracle," which is essentially software that retrieves information from the outside world and integrates it into the blockchain.

Key functions of Chainlink include:
- Listening for data requests
- Extracting information from various suppliers
- Converting off-chain data for on-chain use
- Validating Oracle service performance
- Performing off-chain computations
- Facilitating transactions
- Delivering external data
To implement these functions, Chainlink utilizes a Decentralized Oracle Network (DON), which consolidates data from numerous Chainlink nodes to eliminate single points of failure.
Use Cases for Chainlink
To illustrate this process, consider Chainlink's price feeds, which are among the most recognized sources of oracle support in decentralized finance (DeFi). As of now, Chainlink price feeds secure over $11 billion in assets.
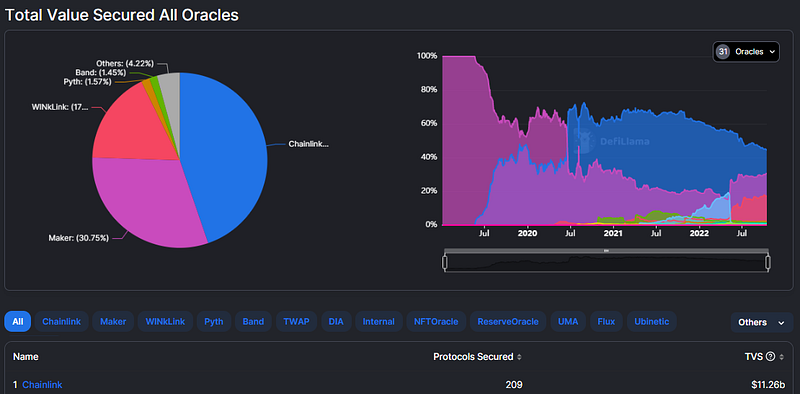
Why are price feeds essential? For instance, if you wish to borrow ETH from Aave, which price should the protocol display? The prices might differ across platforms like Binance, Uniswap, or FTX. Chainlink resolves this by aggregating data through a systematic approach.
- Data Source Aggregation: Firms collect raw market data from multiple sources and create refined pricing datasets available via API.
- Node Operator Aggregation: Each Chainlink node connecting with price feeds retrieves data from various premium aggregators and reports the median price.
- Oracle Network Aggregation: Multiple independent oracles form a DON, regularly generating reports of each node’s median price.
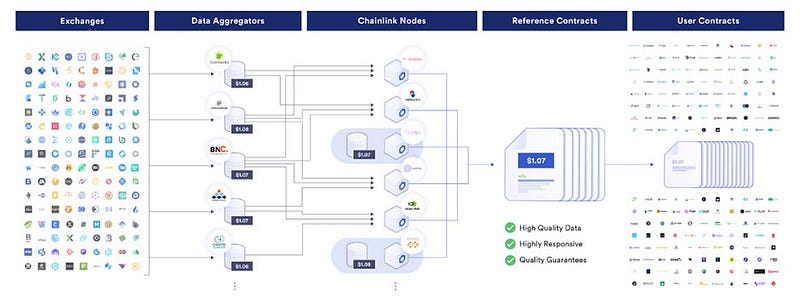
Beyond price feeds, Chainlink's diverse applications include:
- External payments
- NFT and gaming integration
- Enterprise system support
- Weather data aggregation
- Life and health insurance
- Tokenization of tangible assets
Tokenomics Overview
Currently, LINK has a circulating supply of around $500 million, with a maximum cap of $1 billion and a price of approximately $7.00, which is about 86% of its all-time high.
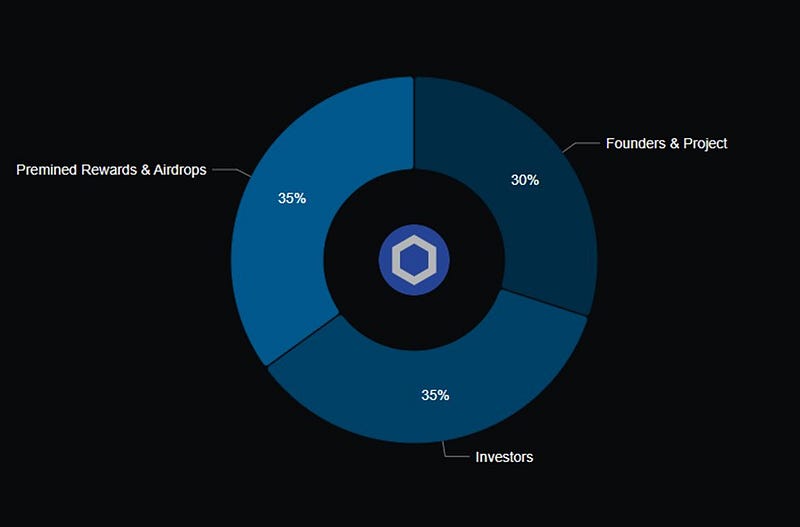
The distribution of LINK is as follows:
- 35% allocated for bounties and airdrops
- 35% reserved for investors
- 30% designated for founders and project development.
LINK serves as a cryptocurrency to fund technology development. Some speculate that this could be a reason for the token's selling pressure, as it's used for development costs. However, this also indicates ongoing advancements in technology.
The Future Outlook for Chainlink
One of Chainlink's strategies to enhance value for LINK holders is through the recent introduction of Staking, which activates four essential catalysts for growth:
- Cryptoeconomic Security: Aspiring oracles must deposit LINK tokens as collateral. Failure to perform adequately may result in losing part of their stake.
- Community Engagement: Users can stake LINK tokens to support the network, with rewards for reporting dishonest nodes.
- Sustainable Rewards: Stakers receive rewards from native token issuances (4-5%) and user service fees, suggesting that increased service utilization leads to higher rewards.
- Empowerment of Node Operators: Staking will determine which nodes can join DONs, giving priority to those with higher stakes.
Moreover, Chainlink's Cross-Chain Interoperable Protocol (CCIP) allows smart contracts to function across various blockchain networks. This has drawn interest from SWIFT, which manages transactions worth $5 trillion daily, envisioning the use of CCIP for enhanced interoperability.

In conclusion, Chainlink represents a vital technology for the blockchain ecosystem. As discussed, the extensive use cases and real-world integration are significant. Its position between the web2 and web3 worlds is strong, and growth potential is clear. However, similar to ATOM, its tokenomics raises questions about LINK's investment viability. Nevertheless, with this new economic framework, several catalysts suggest promising future demand, ongoing development, and enhanced user involvement.
In this video, "Tokenizing Real-World Assets On-Chain | Chainlink Tech Talk #10," the speaker dives into how Chainlink facilitates the tokenization of real-world assets, showcasing real-world applications and innovations that leverage Chainlink's technology.
The video "What is Chainlink? LINK Explained Simply (ANIMATED)" provides an engaging and straightforward explanation of Chainlink's functionalities and its significance in the blockchain landscape.